Lymphatic Health involves the the lymphatic system, which is a network of tissues and organs that help the body fight infection and disease, and maintain fluid levels.
Your lymphatic system has many functions. Its key functions include:
- Collecting excess fluid from your body’s tissues and returning it to your bloodstream. This supports healthy fluid levels in your body. Your lymphatic system also filters out waste products and abnormal cells from this fluid.
- Helping your body absorb fats. Most nutrients can travel through tiny openings (pores) in the walls of your capillaries, and your body can then absorb and use them. But certain fats and other molecules are too large to travel in this way. Your lymphatic system collects fluid from your intestines that contains these molecules and transports it back to your bloodstream.
- Protecting your body against invaders. Your lymphatic system is part of your immune system. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. These cells look for and destroy invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi — that may enter your body.
How does the lymphatic system work?
Every day, more than 5 gallons of plasma (the liquid part of your blood) flow out of tiny pores in the thin walls of your capillaries.
Imagine water seeping out of a sponge. Where does this liquid go? It delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues surrounding each capillary.
The tissues hungrily soak up all the nutrients while leaving behind waste (like a kid who finishes their food but leaves behind a pile of sticky napkins).
The plasma doesn’t mind cleaning up the mess — it picks up the waste and then returns to your bloodstream the same way it came, by flowing back through the pores in your capillary walls. Each day, about 4.5 gallons of plasma return to your bloodstream in this way. Since 5 plus gallons initially flowed out of your capillary walls, that means almost a gallon is still roaming around in your body’s tissues.
That’s where your lymphatic system steps in. Tiny lymphatic capillaries pick up this remaining fluid from your tissues. The fluid changed its name during its journey: now instead of plasma, it’s called lymph. Your lymphatic capillaries move the lymph into larger tubes called lymphatic vessels.
These vessels keep the lymph moving until it ultimately reaches one of two major ducts in your upper chest. These are called your right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct, and they’re a bit like highway on-ramps. They merge into large veins called your subclavian veins and empty the lymph into them. From there, your lymph reenters your bloodstream and can flow through your body again.
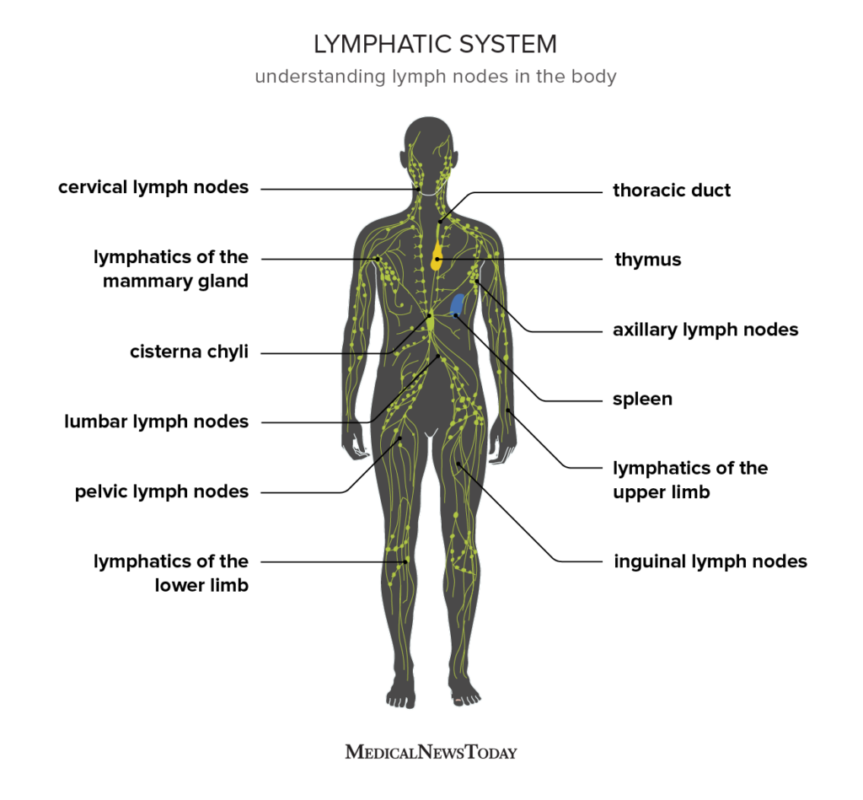
Many different organs and structures make up your lymphatic system. These parts all work together to help keep you healthy.
What are the lymphatic system organs?
The organs of the lymphatic system are your:
- Bone marrow. This is the soft, spongy tissue in the center of certain bones, like your hip bone, backbones and breastbone. Your bone marrow has the vital job of making white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets.
- Thymus. This organ is located in your upper chest beneath your breastbone, and it’s most active before puberty. It’s where T-cells (a type of white blood cell) fully mature. T-cells help your body fight off invaders.
- Lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped glands that monitor and cleanse lymph as it filters through them. They clear out damaged cells and cancer cells. Your lymph nodes also store lymphocytes and other immune system cells that attack and destroy harmful substances like bacteria. You have about 600 lymph nodes scattered throughout your body. Some are closely connected in groups called chains. You may be able to feel some lymph nodes through your skin, in areas like your armpits, groin or neck. Others are deeper inside your body.
- Spleen. This largest lymphatic organ is located on your left side under your ribs and above your stomach. Your spleen filters your blood and removes cells that are old or not working properly. It also keeps red blood cells and platelets available in case your body needs them.
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). This mucus membrane exists throughout your body in many important locations. For example, it lines your tonsils, airways, small intestine and appendix. MALT looks for and destroys germs that could harm you.
Other parts of the lymphatic system?
Your lymphatic system is a big team. Other key players include your:
- Lymph. Lymph, also called lymphatic fluid, is a collection of the extra fluid that drains from cells and tissues in your body and isn’t reabsorbed into your capillaries. Lymph contains many different substances, including proteins, minerals, fats, damaged cells, cancer cells and germs. Lymph also transports infection-fighting white blood cells (lymphocytes).
- Lymphatic vessels. Lymphatic vessels are tubes that form a complex network throughout your body. The smallest tubes are lymphatic capillaries, which ultimately connect to larger tubes that lead to two main ducts in your upper chest. The pulsing of nearby arteries and squeezing of nearby muscles help fluid move through your lymphatic vessels. These vessels contain one-way valves that keep lymph moving the right way.
- Collecting ducts. Two main ducts in your upper chest empty lymph into your subclavian veins. These are your right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct. These ducts are like highway on-ramps or merging points where lymph rejoins your bloodstream.
- Tonsils and adenoids. These structures trap pathogens from the food you eat and the air you take in. They’re part of your body’s first line of defense against invaders. Your tonsils are in the back of your throat. Your adenoids are just behind your nasal cavity but are only active during childhood.
Conditions and Disorders
What conditions and disorders affect the lymphatic system?
Many conditions can affect the various parts of your lymphatic system. Some happen during development before birth or during childhood. Others develop as a result of disease or injury. Some common diseases and disorders of the lymphatic system include:
- Swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy). Infection, inflammation and cancer cause swollen (enlarged) lymph nodes. Common infections that can cause enlarged lymph nodes include strep throat, mononucleosis, HIV and infected skin wounds. Lymphadenitis refers to lymphadenopathy that’s caused by an infection or inflammatory condition.
- Swelling or accumulation of fluid (lymphedema). A blockage in your lymphatic system due to scar tissue from damaged lymph vessels or nodes can cause lymphedema. It can also happen when your lymph nodes have been removed to treat a condition like cancer. With lymphedema, fluid most commonly builds up in your arms or legs. It can be very mild or quite painful and disabling. People with lymphedema are at risk for serious and potentially life-threatening deep skin infections.
- Cancers of the lymphatic system. Lymphoma is cancer of the lymph nodes that occurs when lymphocytes grow and multiply uncontrollably. There are several different types of lymphoma, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancerous tumors can also block lymphatic ducts or be near lymph nodes and interfere with the flow of lymph through the node.
Other disorders include:
- Lymphangitis. This is an inflammation of your lymph vessels.
- Lymphangioma. This is a condition that you’re born with. It involves the presence of noncancerous, fluid-filled bumps (cysts) under your skin due to overgrown lymph vessels.
- Intestinal lymphangiectasia. Loss of lymph tissue in your small intestine leads to loss of protein, gamma globulins, albumin and lymphocytes.
- Lymphocytosis. With this condition, there’s a higher-than-normal amount of lymphocytes in your body.
- Lymphatic filariasis. This is a parasitic infection that causes the lymphatic system to malfunction.
- Castleman disease. Castleman disease involves an overgrowth of cells in your body’s lymphatic system.
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. This is a rare disease in which abnormal muscle-like cells begin to grow out of control in your lungs, lymph nodes and kidneys.
- Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. This is a rare genetic disorder in which there’s a high number of lymphocytes in your lymph nodes, liver and spleen.
- Mesenteric lymphadenitis. This is an inflammation of the lymph nodes in your belly (abdomen).
Protect your Lymphatic System by:
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water to help lymph fluid move through your body. When you’re dehydrated, lymph nodes can swell and not work properly.
- Exercise. Physical activity helps lymph fluid move through your system.
- Deep breathing. Moving your diaphragm muscle through deep breathing helps fluids circulate.
- Avoid toxic chemicals. Avoid exposure to toxic chemicals like those in pesticides or cleaning products.
Dry brushing. Dry brushing with a natural bristled brush can stimulate lymphatic movement. Dry skin brushing benefits may include stimulating the lymphatic system, exfoliating the skin, removing toxins, increasing circulation and energy, and reducing cellulite.
Some signs that your lymphatic system may not be functioning well include:
- Extreme tiredness
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Unexplained swelling that lasts more than a few weeks.
Herbs that work well with the lymphatic health include:
Most Effective
Bittersweet
Highly Effective
Eclipta (Bhringraj)
Effective
- Amana Edulis
- Bladderwrack
- Blueberry
- Bodhi Tree
- Burdock
- Camellia Sinensis (Camellia Sinensis aka Chai aka masala tea)
- Cleavers
- Fimbristylis Ovata is a grass
- Jackfruit
- Marigold
- Menyanthes Trifoliata (bog bean) is an aquatic plant.
- Mimosa Pudica aka Humble Plant is a sensitive creeping weed.
- Nymphaea Odorata (water lily) is an aquatic plant.
- Selaginella doederleinii Hieron belongs to Selaginella genus of the Selaginellaceae family and is commonly used as a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, which was reported to have anti-hyperglycemia, anti-virus, anti-cancer and other pharmacological activities, and used in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Silkworm
- Taro
- Turmeric
- Wintergreen